- Like
- SHARE
- Digg
- Del
- Tumblr
- VKontakte
- Flattr
- Buffer
- Love This
- Save
- Odnoklassniki
- Meneame
- Blogger
- Amazon
- Yahoo Mail
- Gmail
- AOL
- Newsvine
- HackerNews
- Evernote
- MySpace
- Mail.ru
- Viadeo
- Line
- Comments
- Yummly
- SMS
- Viber
- Telegram
- JOIN
- Skype
- Facebook Messenger
- Kakao
- LiveJournal
- Yammer
- Edgar
- Fintel
- Mix
- Instapaper
- Copy Link
Networking Technology: P2P
If you are a regular internet user, you must have encountered the term ‘P2P’ once in your life. Even if you did not come across the term, you may have stumbled upon it practically. Read on to find out the definition of P2P networks, what P2P is used for and examples of P2P networks.
![]()
What is P2P?
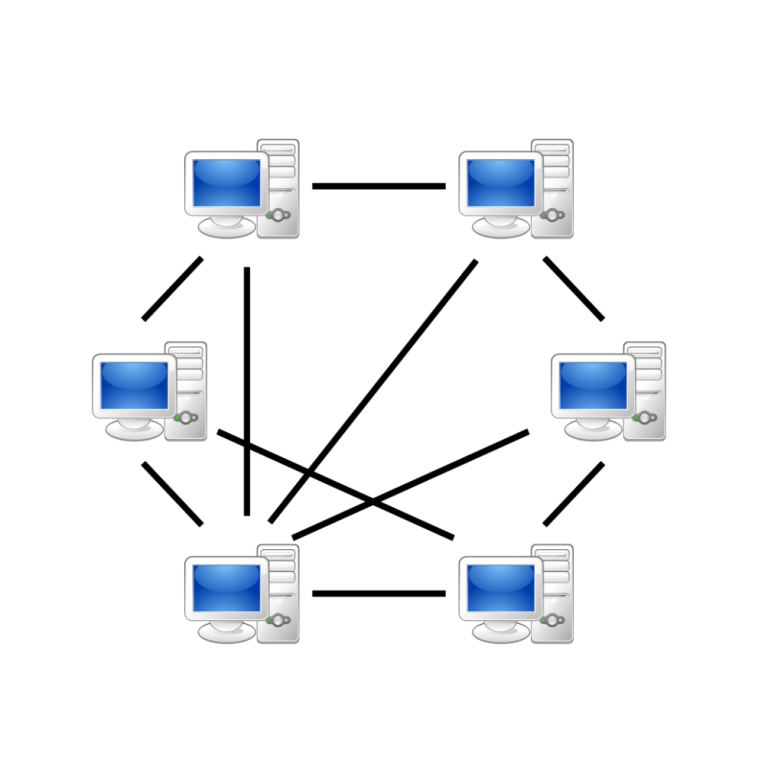
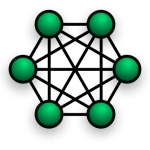
Peer-to-peer (P2P) signifies computer networks which are cooperating with one another in a distributed architecture. Each partner or peer has equal rights in a p2p network and can use the functions of the other partner. While operating locally, data in a peer-to-peer network is distributed by computers linked to the network and not by central servers like on the internet.
Peer-to-peer networks are the most egalitarian networks in the tech world because each peer is equal to the other and has similar duties. Thus, peers are clients and also servers at the same time. P2P networks go back to 1999 when the popular Napster app brought the spotlight on this networking technology. The service allowed users to gain access directly and share files with each other without the involvement of an intermediary server. Since then, many decentralized software and networks have been developed.
Structure of P2P Network
Self organized network (SON) is the simplest to create. Common computer operating systems like Windows support this structure. All the peers in this network can connect with each through LAN or through the internet. Then, each peer identified what files they want to share, password to share so other peers can start mutually sharing files and other resources. This type of network is usually built through the internet and can be secured further through VPN.
Structure of a p2p network with a lot of computers is a bit more complex. These networks are also known as super peer networks running on a user interface as an overlay. The overlay network is managed by the strongest computers in the peer network. The best thing about super peer networks is that any peer can search for files or resources through the search function.
In the cases where two peers directly share files between each other things are simpler. However, torrent technology is used in large sharing networks. Once the data is downloaded in large networks, it is reassembled as the complete file for each peer.
Where Are P2P Networks Typically Deployed?
P2P networks are usually implemented on local networks (like home systems) where devices can be synced with each other for the transmission of data. Network administrators can set these up as wireless or wired networks. In both instances, P2P relies on the same software systems and protocols to conduct their functions. Small businesses and educational institutes often rely on P2P networking to share data among users. In places where a broadband router is used, the created network is referred to as a client-server network or hybrid P2P.
Hybrid P2P environments may include routers that centrally share the network connection. However, the file sharing will be managed by the local PCs connected to the network. Admins can also configure printers and other resources to provide access to every device that’s present on the network.
Uses of peer-to-peer network
Here are the benefits of building a p2p network:
![]()
Easy File Sharing
When you download a file from a p2p network using BitTorrent as a platform, the file is downloaded to your device in bits and pieces saved across the peers on the network. It is like a two-way road because other computers can access the file from your computer as well.
The main goal of p2p networks is to share collective resources and help computers work in collaboration. That is why, p2p networks are also designed to accomplish particular tasks. P2P networks are used to share anything, from files to network bandwidth and even disk storage space. To date, the most important function of this network structure remains to share files on the internet. Peer to peer networks are ideal sources of finding and sending relevant files along.
Affordable
You do not need a separate computer to act as a server in building a p2p server, which is an affordable option.
Reliable and Efficient
In a client server network, the failure of central server can bring down the whole network. P2p networks remain functional even when the central server crashes. As different computers become a part of the network, everyone benefits from their unique resources which add to the efficiency of the entire network.
Adaptability
Peer-to-peer networks adapt to new additions easily which makes them more adaptable than client server networks. Moreover, the network’s efficiency increases as more peers join it.
Criticism on P2P Networks
The most popular criticism on p2p networks is that it is used to share pirated movies, songs and books. For this sole reason, many countries actively work to banish these uploads and downloads. In the United States, popular and big p2p sharing networks have been shut down because they were promoting the sharing of pirated content.
Just like there are two sides of a coin, p2p is a technology which has both benefits and drawbacks. The sanest advice in this regard is to use technology in the right way and not indulge in illicit activities
P2p and Optimization of File Sharing
P2P networks allow file downloads from multiple connected devices. When that happens, small bits of files are scraped from each device and shared simultaneously. This prevents users from having to experience extended download times. Plus, as a P2P network expands, it becomes more efficient at battling hiccups typically experienced in client-server deployments. Also, users are able to see the source of the files as well as the local storage area of their cache.
Overall, P2P networks make it convenient for users to share files and remove the requirement of downloading and uploading files from and to the cloud, reducing redundancy and enhancing efficiency throughout the enterprise.